Building a RAG pipeline often starts with a simple goal, but quickly becomes harder than expected. A small feature can turn into a collection of services, scripts, and configuration files, where minor changes cause frequent failures. What should be an easy way to ground a model in your own data ends up buried under glue code and deployment overhead, making the core idea harder to work with.
This is where n8n, with its RAG capabilities, becomes interesting.
You build the entire RAG pipeline in one visual workflow, choose your models and vector stores, and avoid glue code altogether. The result is a simpler, more reliable way to ground AI in your own data.
Sounds interesting? Let’s take a closer look at how it works!
Why does RAG exist in the first place?
Before discussing the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline, it helps to ask a simple question: what exactly goes wrong when you use a foundation model on its own?
Most teams see familiar patterns:
- The model hallucinated details that do not match reality.
- It did not know the internal data.
- You could not easily update its knowledge without retraining a model.
Imagine your company has product docs, support tickets, and internal guides. You ask a foundation model a question like “Does our enterprise plan support SSO with provider X?” The model has no idea what your plan actually includes, so it guesses based on patterns from the general internet. Sometimes it is close. Sometimes it is dangerously wrong.
You need a way to give the model fresh, trusted context when the question is asked. You also need a way to do this without retraining a model every time your documentation changes.
This is the idea behind RAG pipelines.
What is a RAG pipeline?
A RAG pipeline (Retrieval-Augmented Generation pipeline) is a system that helps an AI model answer questions using your own data, not just what it learned during training.
Instead of asking the model to “know everything,” you let it:
- Retrieve the most relevant pieces of your own data for a given question, on the fly.
- Augment the prompt so the model answers with that context in front of it.
You can think of it as a librarian for your language model. Ingestion is when you bring books into the library. Retrieval is the process of finding the right pages. Augmentation is where you hand those pages to the model.
Key stages of a RAG pipeline
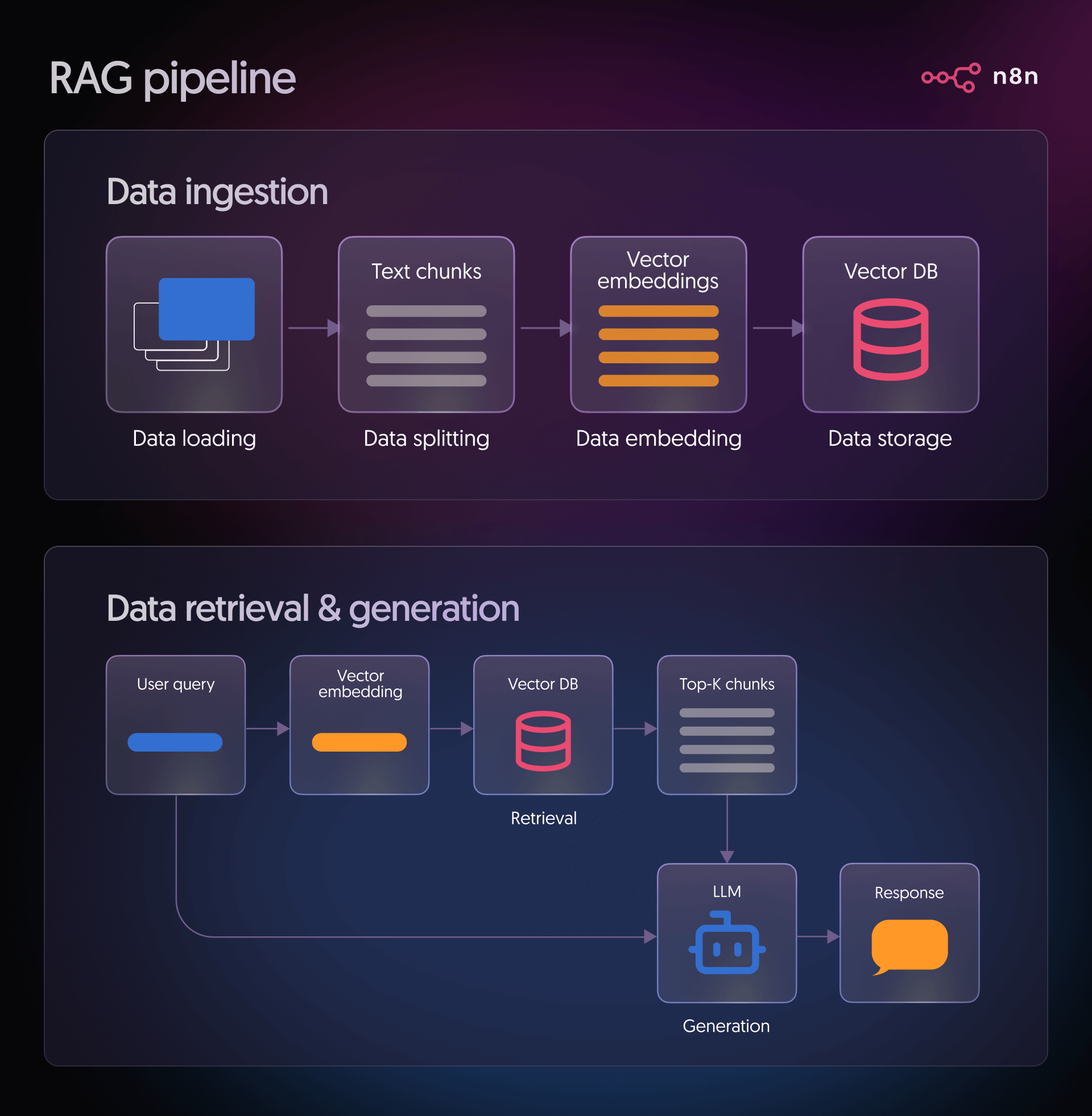
Stage 1: Data ingestion
This stage answers the question “What information should my model have access to?”
Typical sources include product documentation, knowledge base articles, Notion pages, Confluence spaces, PDFs in cloud storage, or support tickets. During ingestion, you:
- Load data: This is the stage where you connect to your chosen source and pull in the documents you want the system to work with. It could be files, pages, or any other text-based content your pipeline relies on.
- Split data: Long documents are split into smaller segments to make them easier for the model to process. These pieces are usually kept below a specific size, for example, around 500 characters, to make retrieval more precise.
- Embed data: Each chunk of text is transformed into a vector using an embedding model. This converts the text's meaning into a numerical form that the system can compare and work with.
- Store data: The vectors are then placed into a vector database. This allows users to quickly find the most relevant chunks when they ask a question.
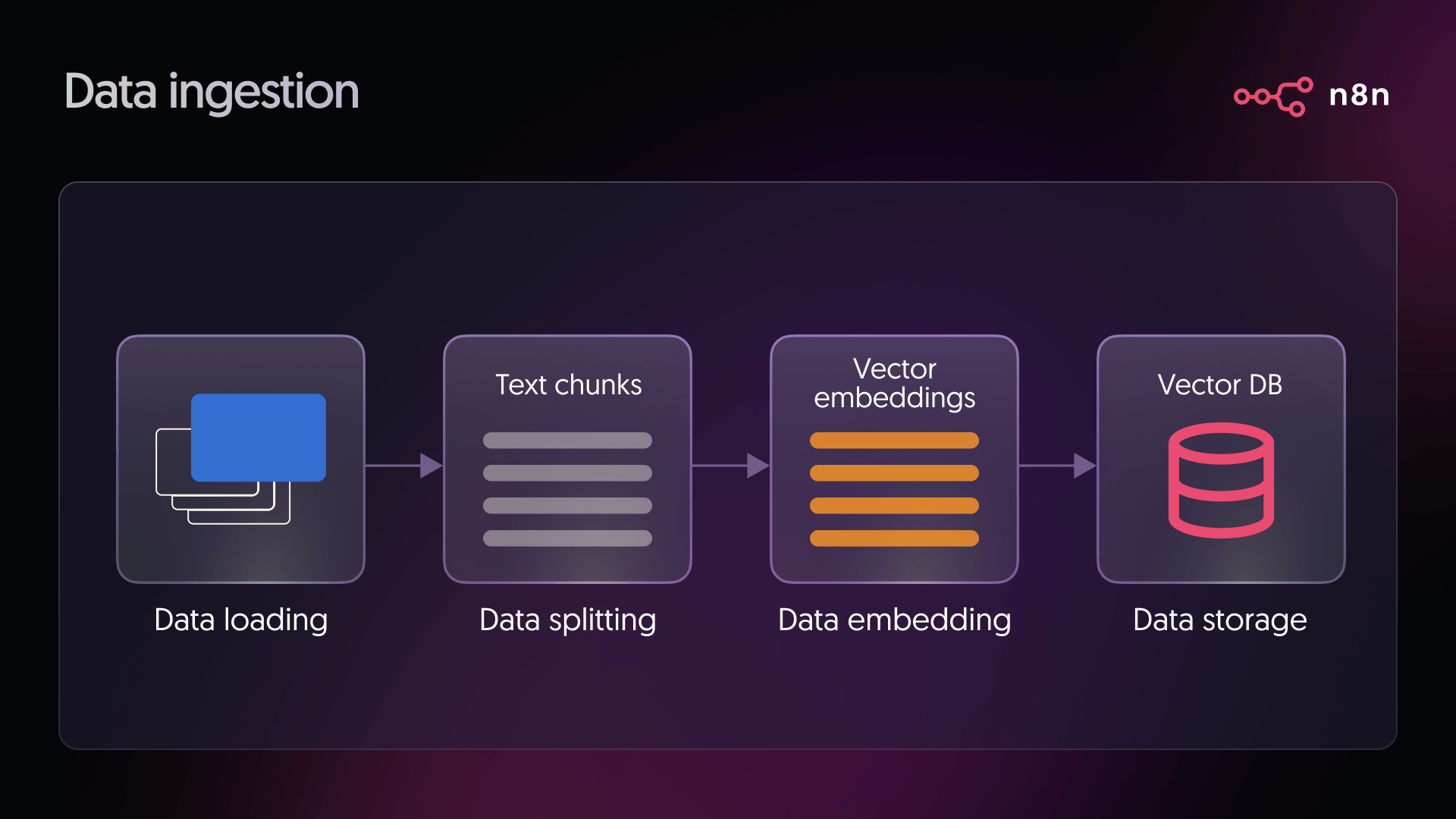
Stage 2: Retrieval, augmentation, and generation
- Retrieval: When a user asks a question, the system converts that question into a vector using the same embedding model used during ingestion. This query vector is then compared against all vectors in the database to find the closest matches. These matches represent the pieces of text most likely to contain helpful information for answering the question.
- Generation: The language model receives two things. The user’s question and the relevant text retrieved from the vector database. It combines both inputs to produce a grounded response, using the retrieved information as context for the answer.
How to build a RAG pipeline in n8n?
We’ll use n8n to illustrate a practical, production-ready approach to building RAG workflows. Instead of focusing on isolated components, n8n lets us design the entire pipeline, from data ingestion and embeddings to retrieval, generation, and post-answer actions, in one place.
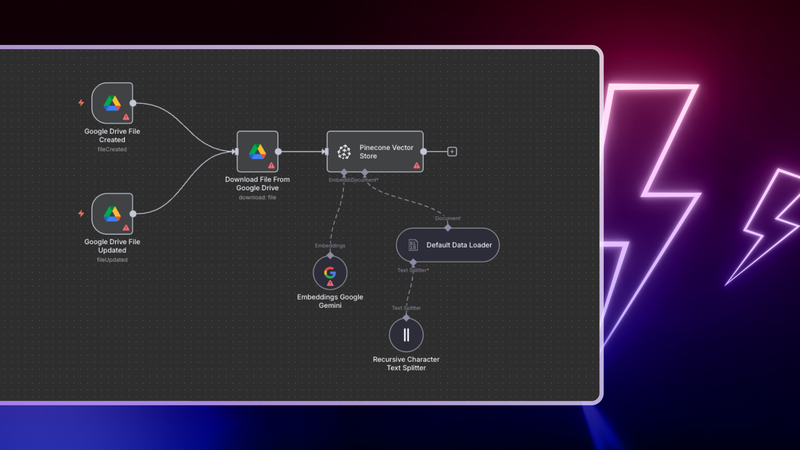
Here's an n8n workflow that listens for new or updated documents in Google Drive, processes them automatically, stores their embeddings in Pinecone, and uses Google’s Gemini models to answer employee questions based on those documents. Everything lives inside one visual workflow. You configure it. You do not write boilerplate code.
Here is what happens behind the scenes:
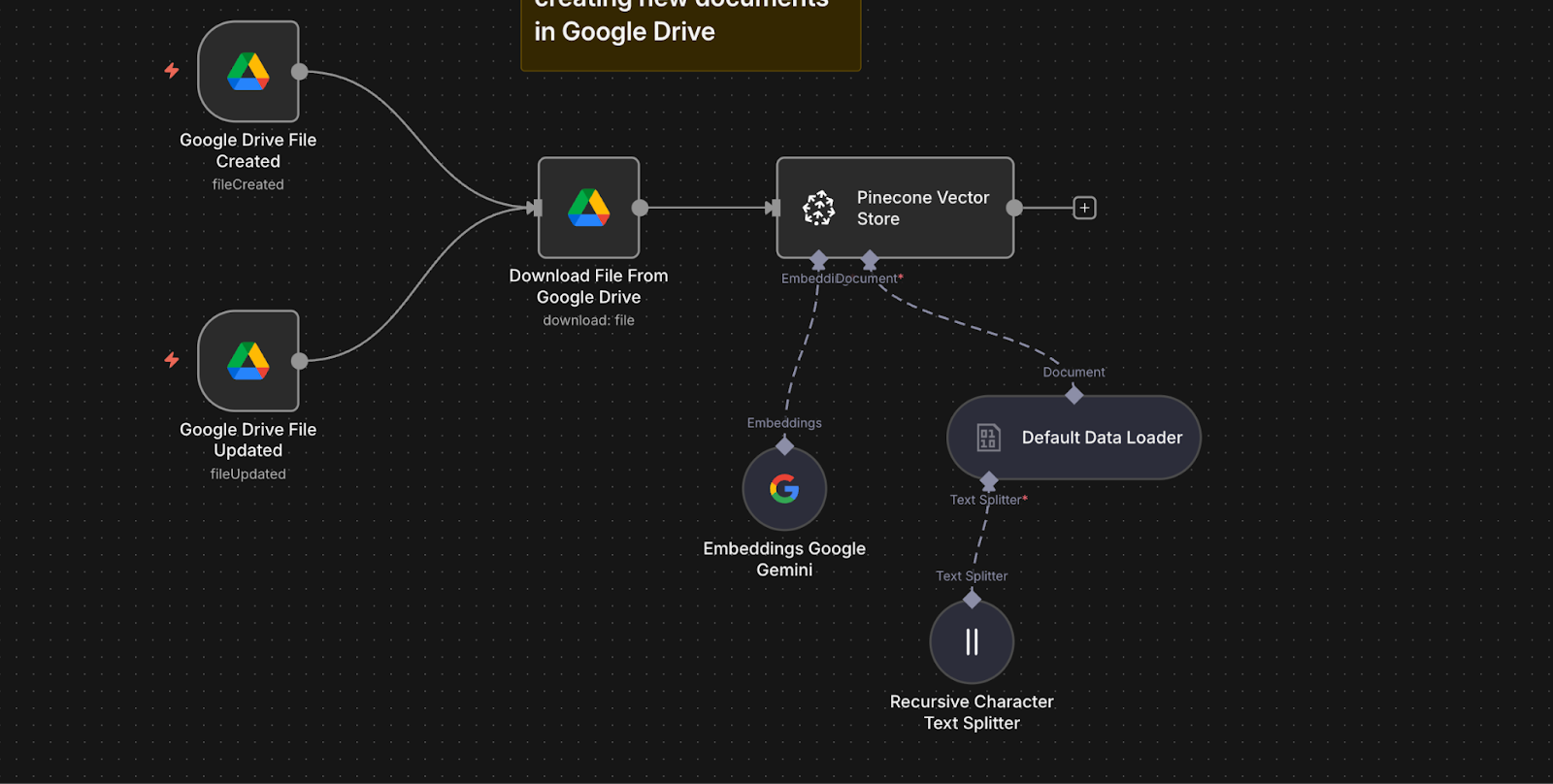
- Two Google Drive Trigger nodes monitor a folder. One detects new files, the other detects updates.
- When a file is detected, a Google Drive node downloads it.
- A Default Data Loader node extracts the document text.
- A Recursive Character Text Splitter node breaks the content into smaller chunks for better retrieval.
- A Google Gemini Embeddings node creates embeddings for each text chunk using the text-embedding-004 model.
- A Pinecone Vector Store node indexes both the chunks and their embeddings into your Pinecone index.
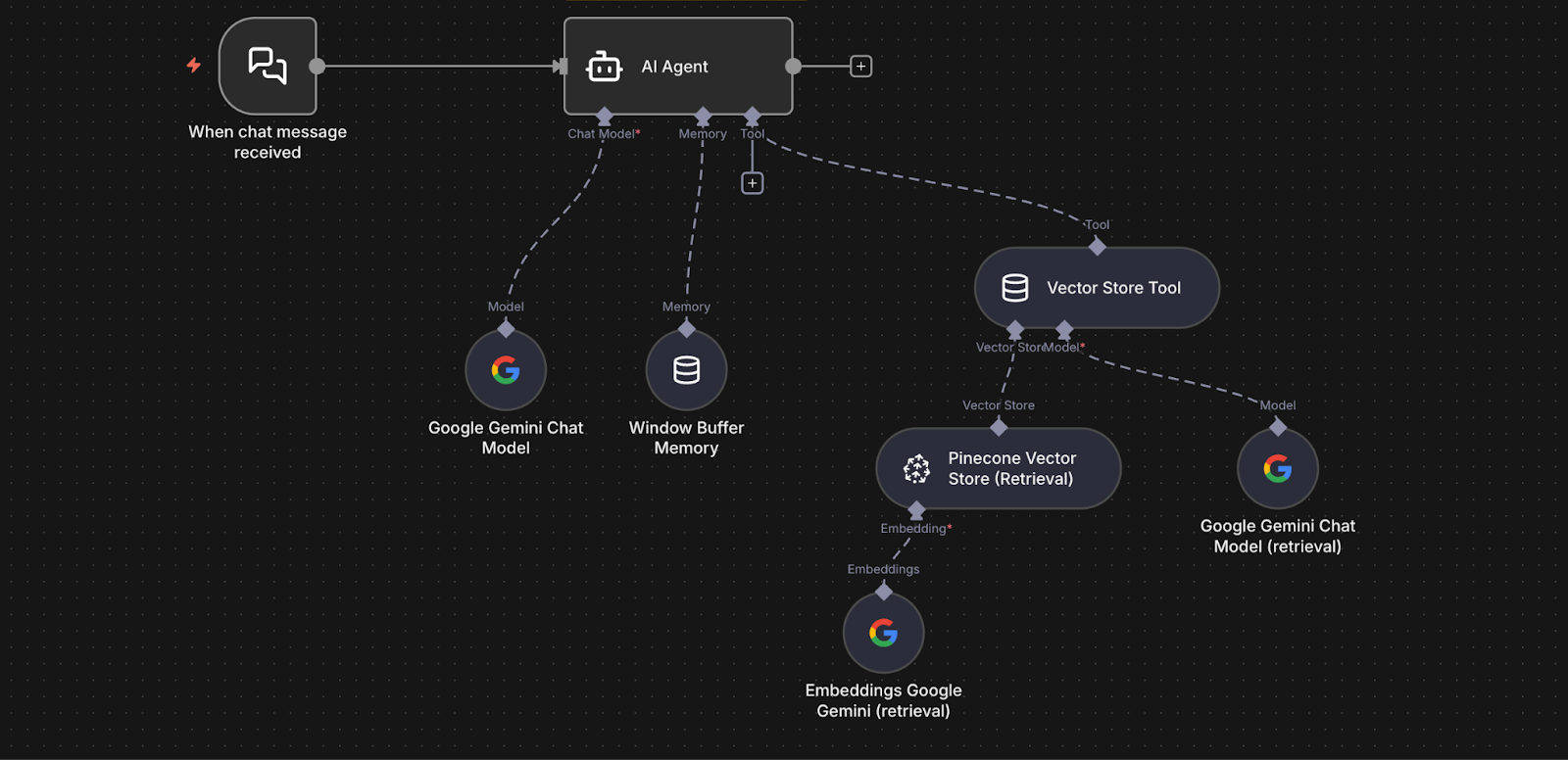
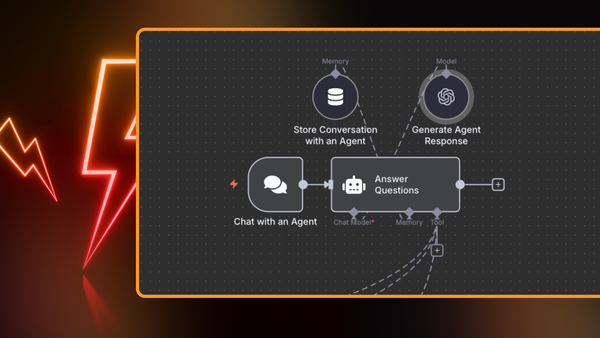
- A Chat Trigger node receives employee questions.
- The question is passed to an AI Agent node.
- The agent uses a Vector Store Tool connected to Pinecone in query mode to retrieve relevant chunks.
- The agent forwards the question and the retrieved chunks to the Google Gemini Chat Model.
- Gemini generates a grounded response using the retrieved text.
- A Window Buffer Memory node allows for short-term conversation memory, so follow-up questions feel natural.
In short, the workflow keeps your document index up to date and uses it to power an intelligent, context-aware chatbot.
To run this RAG workflow in your own n8n instance, you will complete a few setup steps. Each step activates part of the pipeline you saw above.
Step 1: Prepare your accounts
You will need three services set up.
Google Cloud Project and Vertex AI API
- Create a Google Cloud project → https://console.cloud.google.com/projectcreate
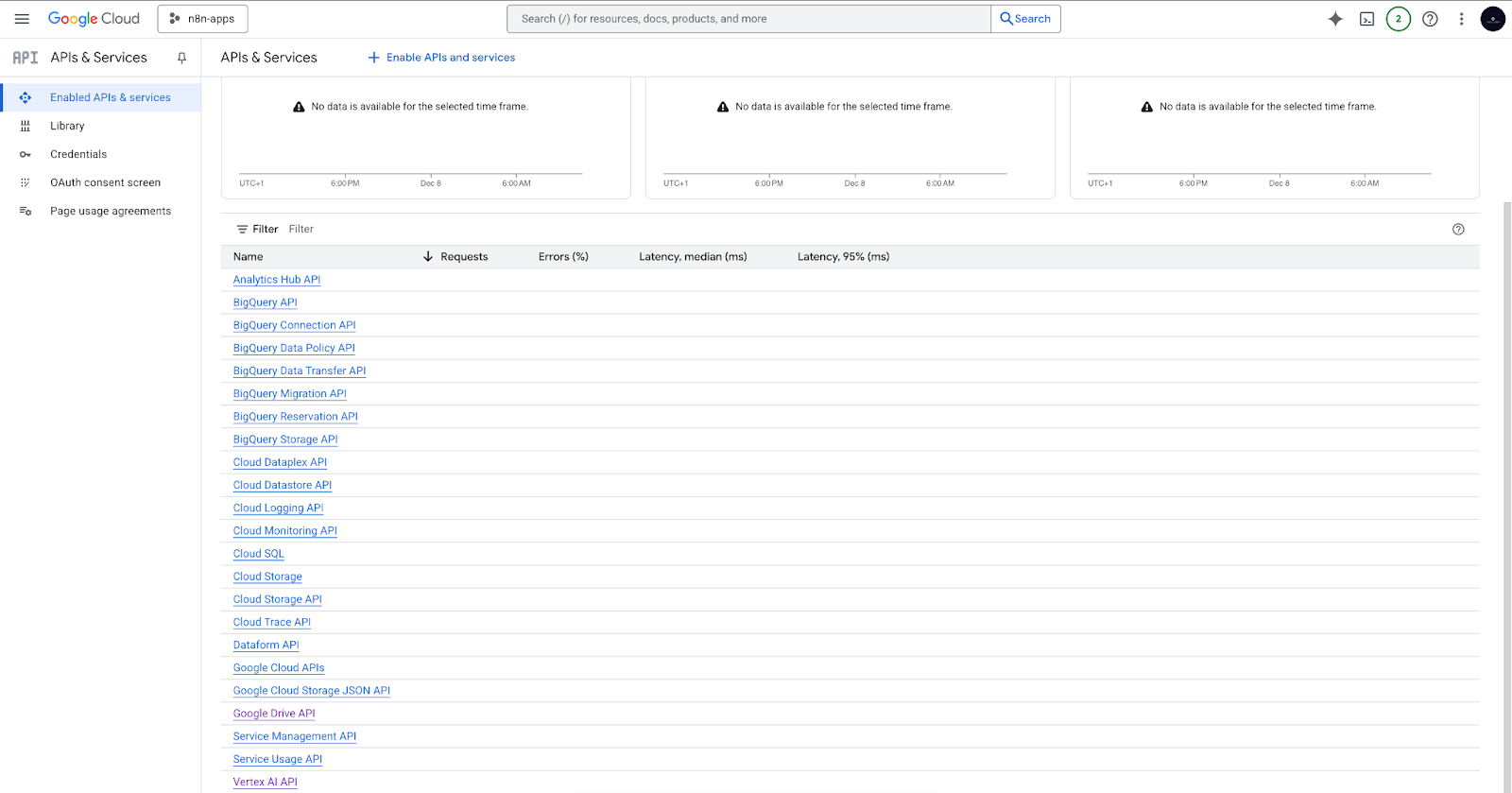
- Enable required services inside the project:
- The Vertex AI API (for embeddings and chat models).
- Enable the Google Drive API (for loading and monitoring documents from Drive).
If all goes well, you should see the Vertex AI API and the Google Drive API in your list of enabled services.
Google AI API key
- Get your API key from Google AI Studio → https://aistudio.google.com/
- This key will authenticate all Gemini model calls from n8n.
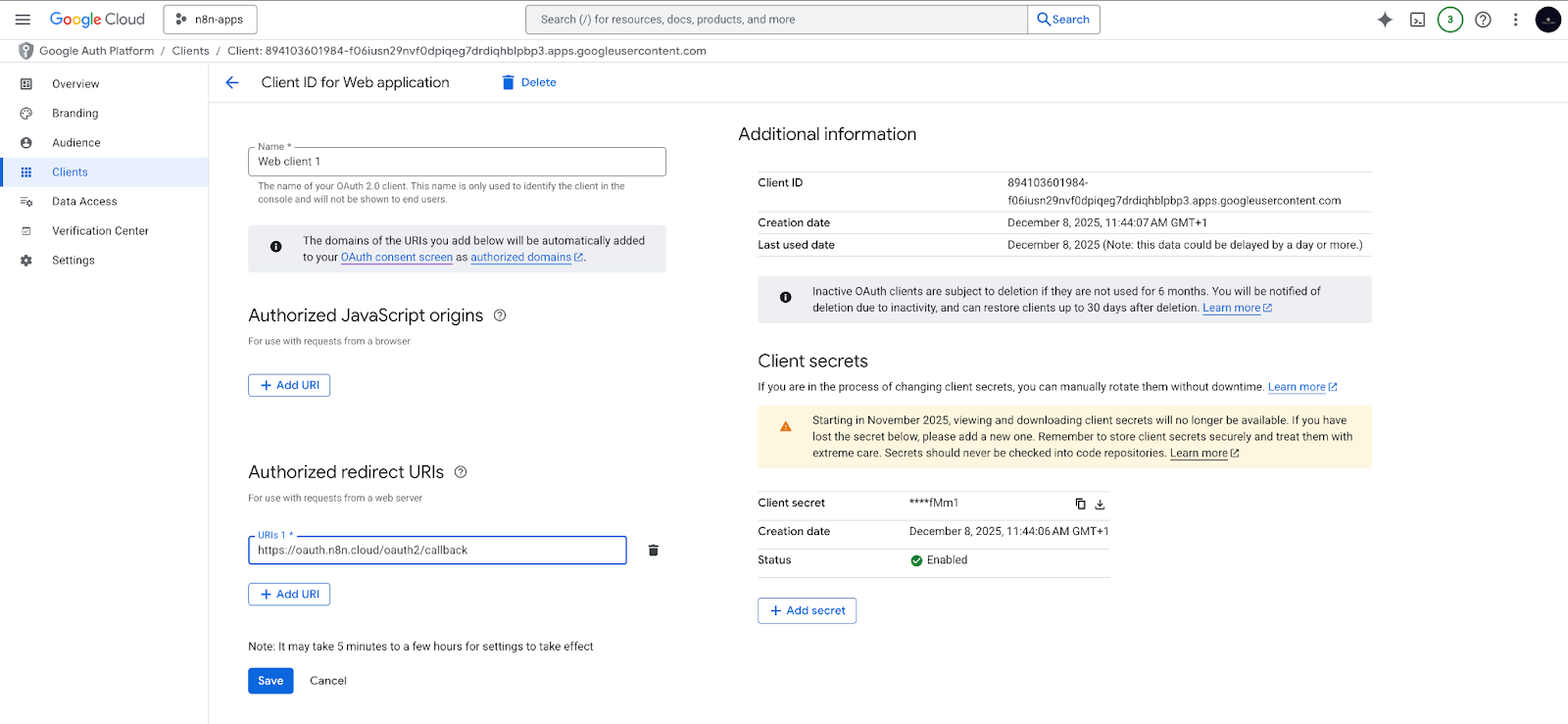
Google Drive OAuth2 credentials
- In your Google Cloud project, create an OAuth2 Client ID.
- Add the correct redirect URI for your n8n instance.
- Use this OAuth2 credential in n8n to give the workflow permission to read your Google Drive folder.
Pinecone account
- Create a free Pinecone account → https://www.pinecone.io
- You will see an existing default API key. Copy it.
- Create an index named company-files to store your embeddings and text chunks.
Step 2: Prepare your Google Drive folder
Create a dedicated folder in Google Drive. This folder will hold all the documents your chatbot should use as references. The workflow will automatically monitor this folder.
Step 3: Add your credentials to n8n
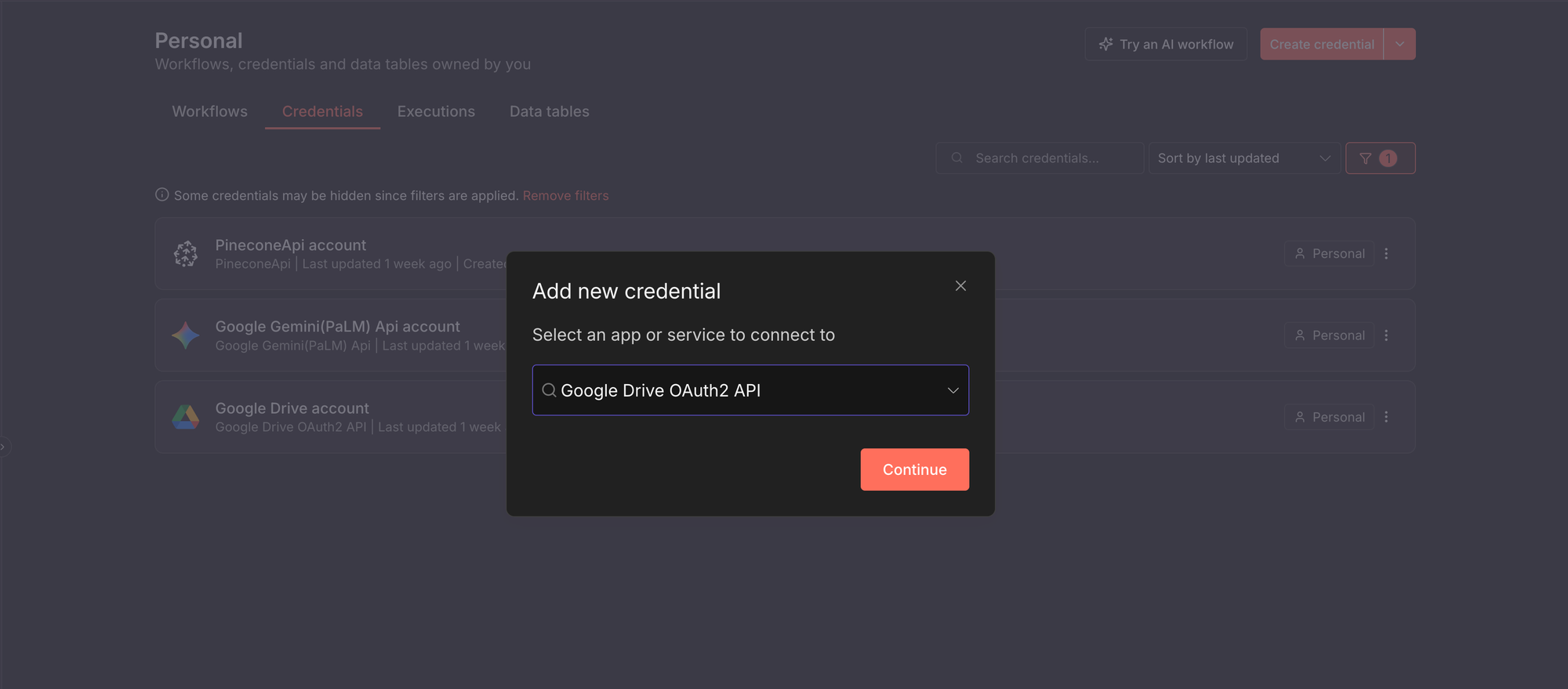
Before the workflow can run, n8n needs permission to talk to external services. You do this by creating credentials. Generally, to add any credential in n8n:
- Open your n8n instance.
- Click Create credential.
- Select the service you want to connect to. In the screenshot below, I selected the Google Drive OAuth2 service.
For this guide, we need to create credentials for three services:
- Google Drive OAuth2
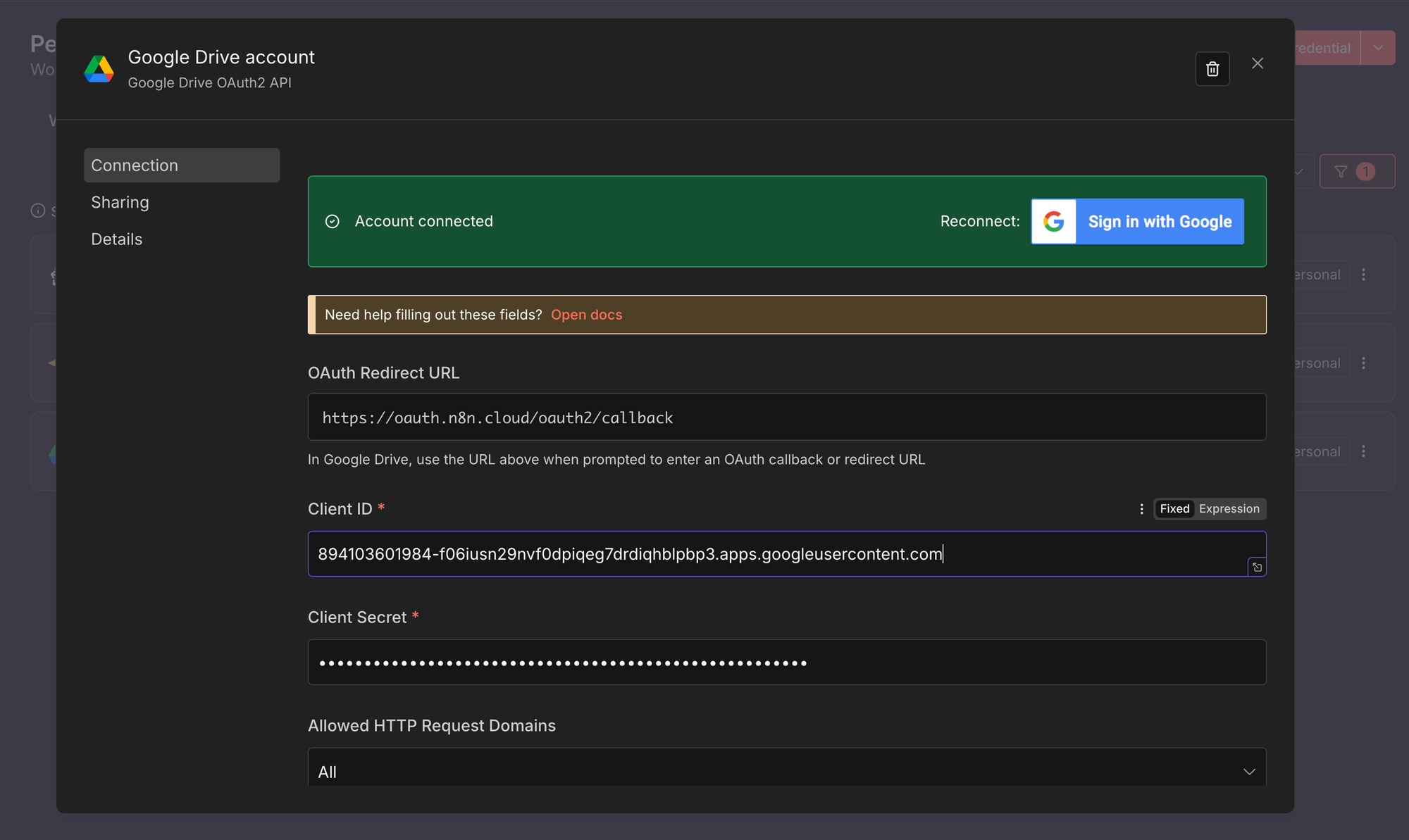
This credential allows n8n to read and monitor files in your Google Drive.
- Create a new credential of type Google Drive OAuth2, following the steps above.
- Enter the Client ID and Client Secret from your Google Cloud project.
- Click Connect and complete the Google authorisation flow.
- Google Gemini (PaLM) API
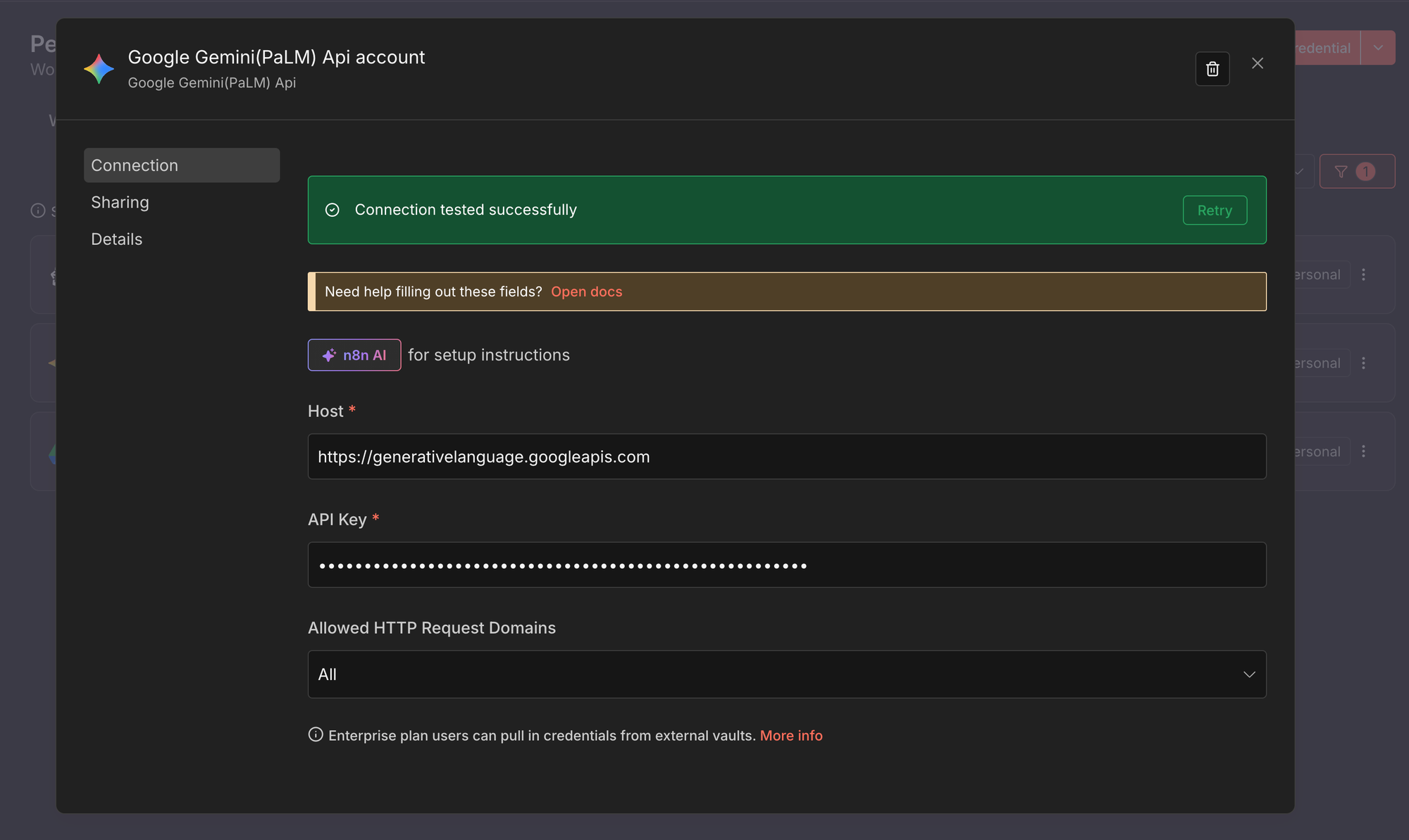
This credential is used for embeddings and chat generation with Gemini models.
- Create a new credential of type Google Gemini (PaLM) API.
- Paste your Google AI API key from Google AI Studio.
- Save the credential.
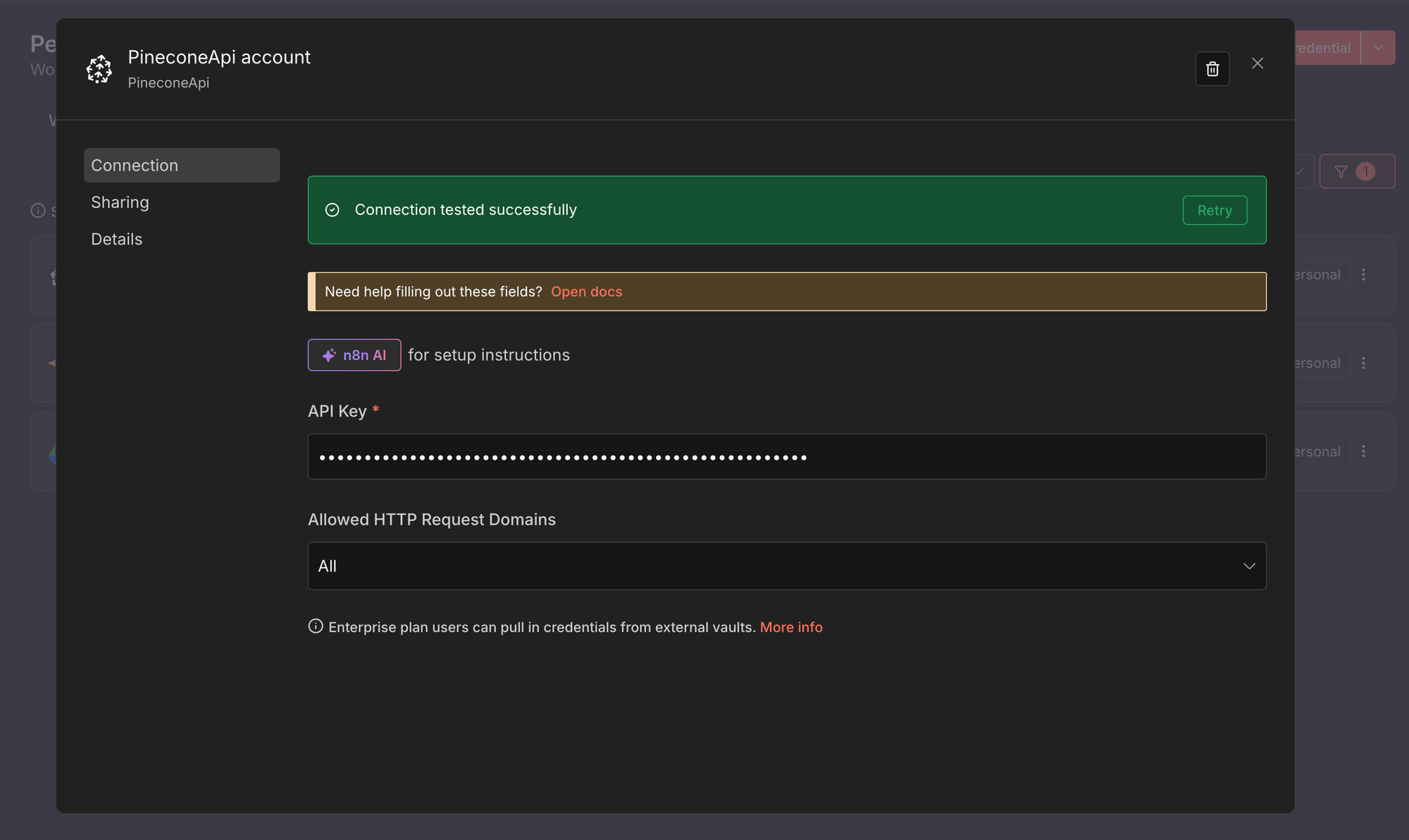
- Pinecone API
This credential allows n8n to store and retrieve vectors from your Pinecone index.
- Create a new credential of type Pinecone API.
- Paste your Pinecone API key.
- Save the credential.
Once created, you can select the credential from any compatible node. For a deeper overview, see the official n8n documentation on credentials.
Step 4: Import the RAG workflow
Download or copy the workflow and import it into your n8n instance. You will now see the full RAG pipeline inside the editor with all nodes connected.
Step 5: Configure the nodes
Make the workflow yours by updating a few nodes.
- Update both Google Drive Trigger nodes to watch the folder you created.
- Open the Pinecone Vector Store nodes and point them to your company-files index.
- Confirm the embedding model settings in the Embeddings Google Gemini node.
- Confirm the chat model selection in the Google Gemini Chat Model node.
At this point, your workflow is fully wired to your accounts, your Drive folder, and your vector index.
Step 6: Test the RAG pipeline
Add or update a document in your Google Drive folder to trigger the indexing flow. Then ask a question through the chat entry point and observe how the agent retrieves relevant text and generates an answer. Every step is visible in n8n, so you can easily inspect and debug.
Step 7: Activate the workflow
Enable the workflow in n8n Cloud or run it in your self-hosted environment. Your RAG chatbot is now live, indexing new company documents automatically and answering employee questions with grounded, up-to-date information.
What are 5 RAG pipeline examples in n8n?
Now that you’ve seen how a RAG pipeline fits together in n8n, it helps to look at real examples. The following workflows show different ways teams use RAG in practice, from simple starters to more advanced, automated setups.
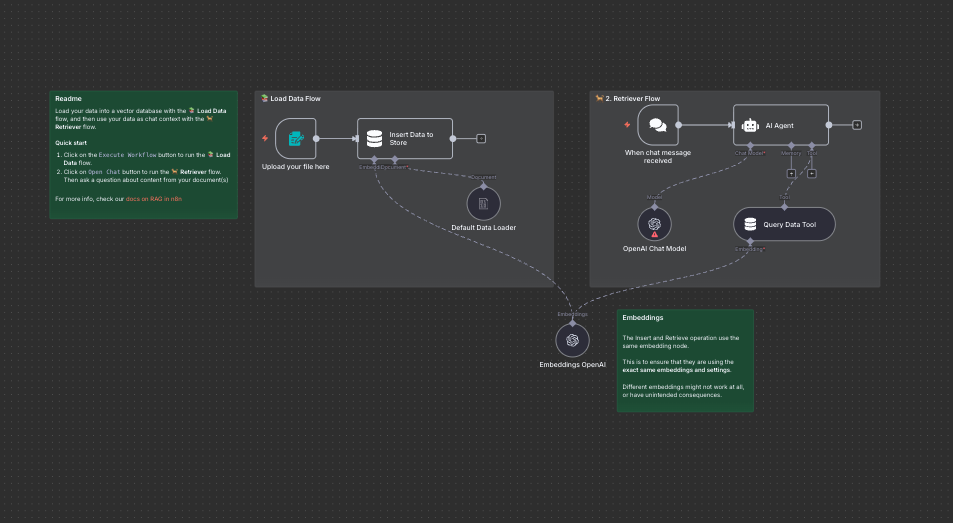
RAG starter template using simple vector stores and form trigger
A beginner-friendly RAG workflow that shows how to give an agent knowledge from a PDF or document. Upload a file, generate embeddings, and start chatting with your content using a simple vector store:
Build custom workflows automatically with GPT-4o, RAG, and web search
This template shows how to convert a one-line request into an automated n8n workflow with RAG and web search capabilities. It’s ideal for quickly prototyping complex automations with little manual wiring.
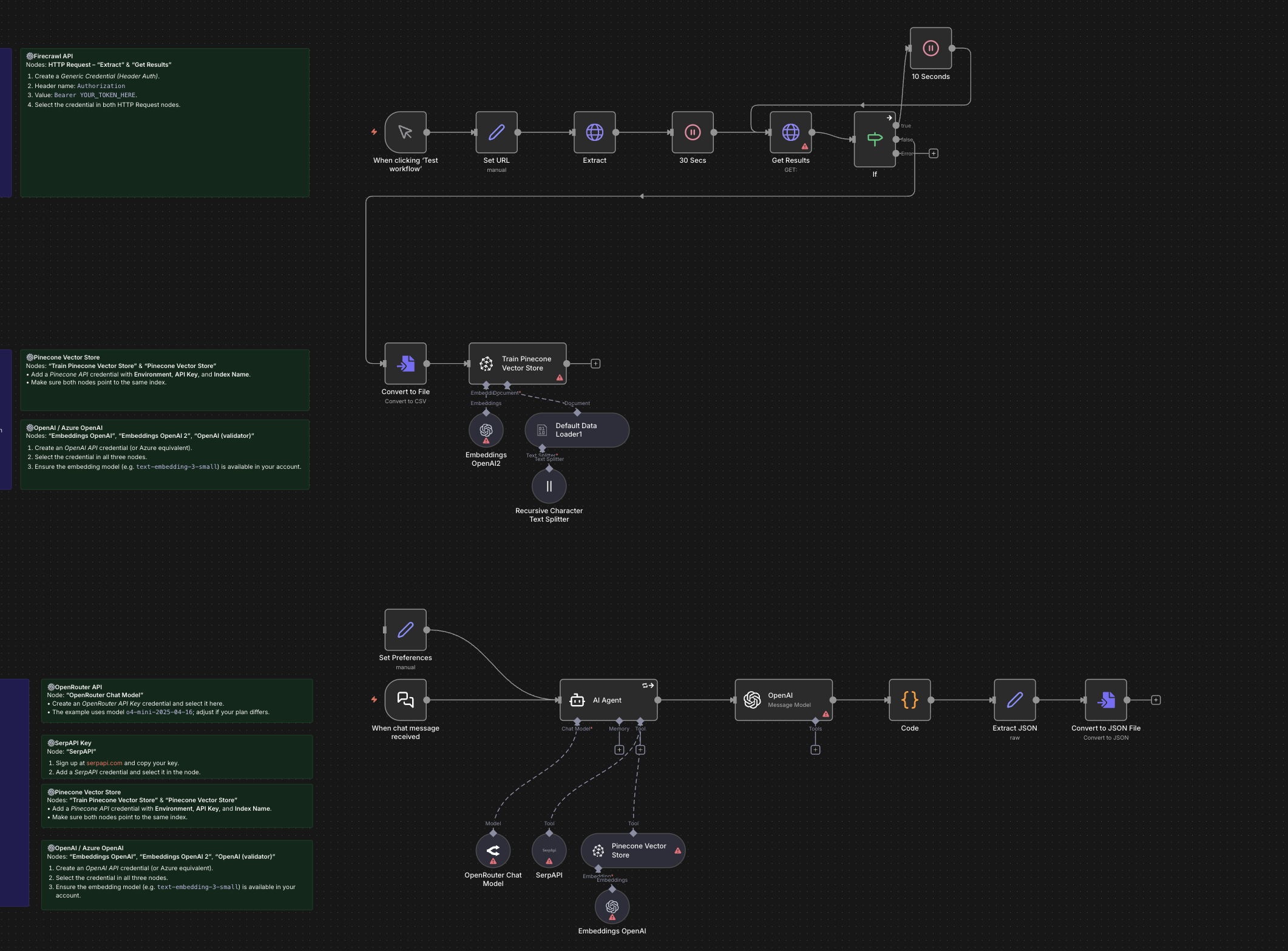
Create a documentation expert bot with RAG, Gemini, and Supabase
A hands-on workflow that builds a RAG chatbot knowledgeable about a specific topic by indexing documentation and serving as an “expert librarian” that answers questions with grounded context.
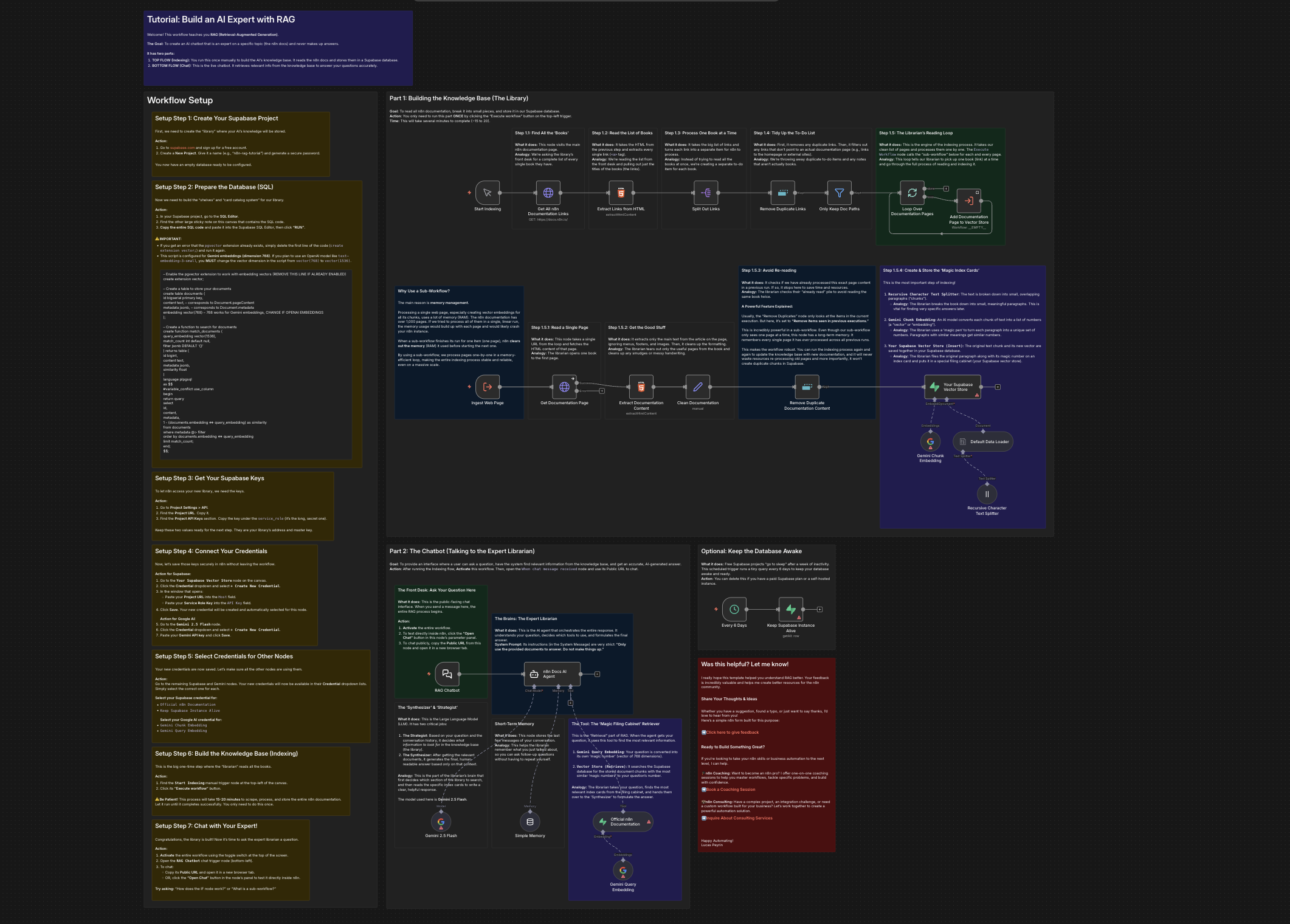
Basic RAG chat
A simpler RAG example that demonstrates an end-to-end pipeline using an in-memory vector store for quick prototyping. It shows data ingestion, embeddings with an external provider, retrieval, and chat generation.
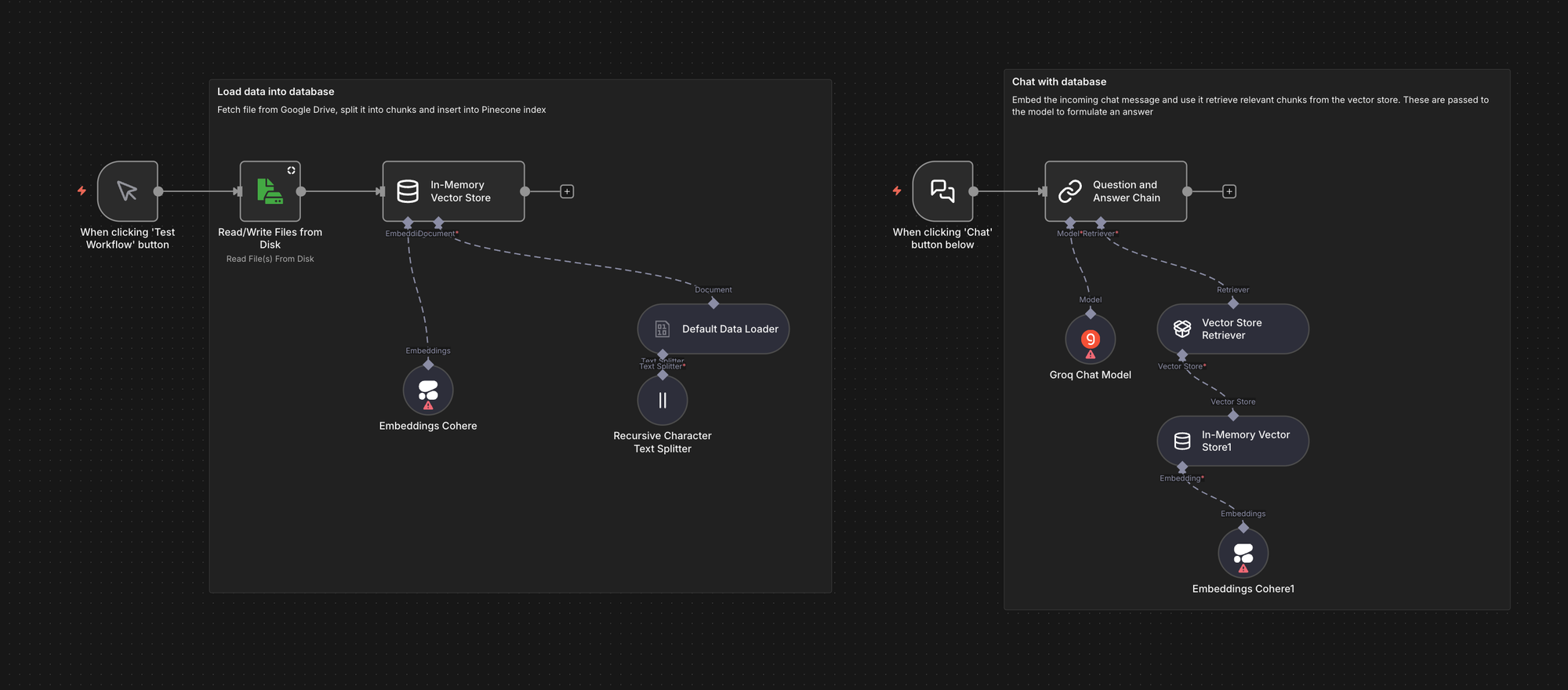
Local chatbot with Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
This workflow shows how to run a fully local RAG chatbot using n8n with Ollama and Qdrant. It ingests PDF files into Qdrant, retrieves relevant chunks at query time, and answers using a local model, which is useful when you want RAG without sending data to external APIs.
Benefits and challenges of RAG
RAG offers clear benefits, from reducing hallucinations to making knowledge reusable across teams, but it also introduces new challenges around data quality, performance, and security. Understanding these trade-offs is essential before building, and n8n provides a practical way to manage them in one system.
Benefits
- RAG reduces hallucinations by grounding answers in your real data.
- It enables easy updates without retraining.
- It makes your knowledge reusable by letting multiple teams pull from the same indexed documents.
- It speeds up experimentation by letting you change models or data sources without rewriting code.
Challenges
- RAG depends on the quality of your data.
- Chunking and retrieval may need tuning when your documents vary in structure or when the retrieved text is not specific enough to answer the question.
- The pipeline can introduce latency when documents are large or when your vector store is slow to respond.
- You must also consider security because your embeddings and stored chunks may contain sensitive internal information that must be protected.
Frequently asked questions about RAG pipelines
How does a RAG pipeline in LangChain compare to building one in n8n?
LangChain is excellent when you want complete control through code. It gives you fine-grained tools for chunking, embedding, retrieval, and orchestration. n8n gives you the same core pattern in a visual flow, with little to no code.
Can I still use Python if I build my RAG pipeline in n8n?
Yes. You can keep Python for the pieces that genuinely need it. n8n takes over the routine parts of ingestion, embeddings, vector search, and model calls, so you write fewer maintenance scripts. When a custom transformation or scoring function is needed, you can use the Code node to run a small Python snippet and feed the result back into the workflow.
Do I need code at all to build a RAG pipeline?
You do not need code to build the core pipeline. Ingestion, splitting, embeddings, vector storage, retrieval, prompting, and generation can all run visually in n8n. Code becomes optional. You add it only for advanced logic specific to your organisation.
How does a Haystack-based RAG pipeline fit with n8n?
Haystack is a strong framework for retrieval, ranking, and search in Python. You can keep Haystack for specific retrieval logic and let n8n handle the surrounding orchestration. n8n can trigger Haystack jobs, pass documents or queries into the pipeline, handle retries, and connect results to downstream systems. Some teams replace Haystack entirely with visual nodes to simplify maintenance.
Wrap up
RAG exists because foundation models alone cannot reliably answer questions about your internal data.
In code-heavy setups, a RAG pipeline requires many custom services and scripts. In n8n, you use ready templates and visual nodes to build and deploy a RAG pipeline with little or no boilerplate code. You keep control, clarity, and flexibility without drowning in setup.
What's next?
If you want to dive deeper into RAG pipelines and n8n, please see our RAG documentation. Additionally, the resources below go beyond the basics. They walk you through full pipelines, show real setups, and explore more advanced automation patterns.
- There’s a broader shift toward agentic RAG workflows — systems that don’t just retrieve and answer, but verify, refine, and improve their own results. This guide focuses on the foundation, but once that’s stable, the next step is teaching your pipeline to evaluate and strengthen its own output.
- Build custom RAG chatbots with n8n: A detailed article that explains how to connect any knowledge source, index it in a vector database, and build an AI-powered chatbot using n8n’s visual workflows.
- Index documents from Google Drive to Pinecone with n8n: A ready-to-use workflow template that watches a Drive folder and automatically indexes new files into a Pinecone vector store. Great starting point for doc-based RAG systems.
- Creating a RAG Agent in n8n for Beginners: A comprehensive step-by-step guide.
The best RAG pipeline is the one shaped by your data and your needs. These resources give you a toolkit for building, improving, and scaling. n8n makes it possible, without overwhelming boilerplate!