AI agents sound revolutionary until you try to build one for your business. Suddenly, you're faced with unpredictable LLM outputs, integration challenges, and a gap between demo-ready prototypes and production-ready systems.
The right AI agent builder bridges this gap by providing the infrastructure, integrations, and control mechanisms that enterprises need.
In this guide, we'll look at 7 platforms that go beyond basic chatbots to automate real business processes using AI.
Here's what we'll cover:
- What are AI agent builders?
- AI agent builder types
- Why use AI agent builders?
- What is the best tool to build AI agents?
- How to choose an AI agent builder?
- Wrap up
- What's next?
What are AI agent builders?
The bare-bones way of building an AI agent is by hard-coding it.
If you want to use an abstracted AI agent builder to make the process quicker and easier to maintain, you can choose from the following:
- Workflow-based builders
- AI native workflow builders
- Workflow builders with AI retrofitted
- Non-workflow builders
AI agent builders are specialized platforms for building, deploying and managing AI-powered agents without having to build everything from scratch. These tools provide the infrastructure and interfaces needed to combine LLMs with business logic, external integrations and deterministic workflows to create reliable AI systems.
Unlike traditional automation tools that follow rigid ‘if-then’ rules, AI agent builders combine the reasoning capabilities of LLMs with the guardrails and integration capabilities enterprises need. Additionally, such tools ensure structured outputs and predictable behavior required for business-critical applications.
AI agent builder types
AI-native workflow builders
These are mostly startups that have built their platform extensively (and exclusively) to build AI agents.
These include tools like Vellum, Dify, Langflow, Flowise, with their primary focus on building AI agents. They provide users with a great deal of control over agents’ behavior, but make it harder to integrate with their IT stack. They are better suited for use cases where Agents access web resources, SaaS apps, and documents rather than coordinating a bunch of on-premises enterprise applications.
Workflow builders with AI retrofitted
These vendors found themselves in a great position to hop onto the biggest bandwagon of the 2020s.
Workflow automation tools have some distinct maturity advantages, particularly around depth and breadth of integrations, which provide tried-and-tested methods of bringing a tech stack together without writing custom connectors for each application. Native Agentic AI dev tools, on the other hand, have the agility advantage and don’t have to retrofit AI to an existing product.
Writing integrations, engaging with technology partners, building a community, and offering out-of-the-box content are very long exercises. It is not an apples-for-apples comparison to look at a 2024-established Stack-AI against a 2013-established Camunda in terms of the integrability features. Tools that score well in integrability and lower in codability are also great contenders for less complex agentic systems.
If you don’t need to have orchestrated multi-agents working in parallel, but still need to integrate with your wider system, these tools may very well be fully satisfactory.
Workflow-based agent development tools are:
- Restrictive - these agents still have self-determination, but they naturally give you a way of interacting with the LLM output
- Low technical knowledge - no-code interfaces are much more intuitive for citizen developers. While code-based capabilities still exist, they are mainly used as a fall-back for instances when the no-code GUI doesn’t support a use case.
- Automating pre-existing processes - writing workflows inherently requires a workflow to exist. Even a self-determining agent must be defined within a given framework or business context.
- Expose Agents to end-users - with the appropriate guardrails, a workflow-based agent can be exposed to end-users, which includes support and sales bots.
Non-workflow-based AI builders
These include tools such as LangGraph, Restack, Autogen, and others.
Non-workflow-based agent development tools are:
- Permissive - they provide agents a greater deal of autonomy and self-determination, which is particularly useful for reasoning models
- Higher technical knowledge - they require users to have a better understanding of how LLMs work and at least a high-level knowledge of coding practices (i.e. how to define a condition, what an API key is, what’s an URL)
- Supporting novel use cases - they are best used for processes that don’t follow standard operating procedures and perhaps for ad-hoc requests. For example, asking in natural language what the overall customer sentiment is in support chat, and comparing it with sentiment across social media.
- Mainly for internal use cases - less risky to deploy without some serious deterministic guardrails, which are needed for customer-facing solutions.
Why use AI agent builders?
Building AI agents from scratch requires significant technical expertise and development time that most organizations can't afford. AI agent builders significantly reduce this complexity by providing pre-built components, integrations and orchestration capabilities.
- Accelerated time-to-market is perhaps the most compelling benefit, as these platforms allow teams to move from prototype to production in weeks rather than months. They provide the infrastructure needed for reliable AI systems, including error handling, state management, and integration capabilities that are essential for enterprise deployments.
- Enterprise-grade reliability comes built-in, with features like human-in-the-loop controls, audit trails, automatic model evals and deterministic logic that ensure AI agents behave predictably in business-critical scenarios. This is crucial because the non-deterministic LLMs require careful orchestration to be suitable for enterprise applications.
- Cost efficiency is another major benefit, as organizations can avoid building custom solutions for common requirements like database connections, API integrations and workflow orchestration. This allows teams to focus on their unique business logic rather than infrastructure concerns.
What is the best tool to build AI agents?
We’ve selected 7 AI agent builder platforms representing the current state of enterprise AI agent development. For this article, we’ve prioritized tools with distinct characteristics and approaches to ensure coverage of different team skillsets, use case complexities and organizational requirements.
| Tool | Best For | Unique Features | Language | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n8n | 🔄 👨💼👩💼 Flexible workflows + AI automation with 400+ integrations |
Visual workflows + code, 1000+ community nodes |
JavaScript/ TypeScript Python support |
From $24/mo on cloud Free Community version |
| Dify | 🔄 👨🎓 Rapid AI app prototyping with minimal setup |
Pre-configured AI features, built-in publishing |
Python | Free cloud Sandbox From $59/mo on Pro tier free community version |
| Vellum | 🔄 👨💼👩💼 Production-grade AI development with enterprise features |
Code-interface sync, built-in evaluations |
Python TypeScript |
Custom pricing 7-day free trial |
| Camunda | 🔄 👨💻 BPMN business processes enhanced with AI capabilities |
BPMN notation, mature process automation |
Multiple | Free dev version custom Enterprise tier |
| LangGraph | ⚙️ 👨💻 Complex stateful agents with maximum developer control |
LangChain ecosystem, stateful workflows |
Python JavaScript |
Limited free tier From $39 per seat/mo Custom Enterprise tier + usage costs |
| Restack | ⚙️ 👨💻 Production-ready agents with long-running processes |
Dual process theory, failure recovery |
Python TypeScript |
Per-seat + compute open-source option |
| Autogen | ⚙️ 👨💻 Multi-agent conversations and research applications |
Multi-agent coordination, Autogen Studio |
Python .NET |
Free open-source |
n8n
AI agent builder type: Workflow-based agent builder
Best for: creating flexible solutions with both classical workflows and complex AI automations
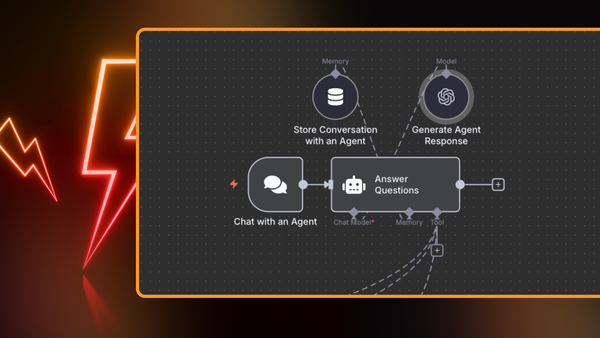
n8n is a powerful source-available automation platform that uniquely combines traditional workflow automation with advanced AI agent capabilities. n8n offers both self-hosted and cloud deployment options, making it accessible to organizations with varying infrastructure requirements. The platform provides a visual workflow builder, as well as custom coding in JavaScript or Python.
Unique capabilities
- Workflow automation and complex AI agent development on a single platform;
- Integration ecosystem with over 400+ pre-built connectors;
- Allows you to start with drag-and-drop and gradually add code as needed.
Limitations
- Steeper learning curve compared to more opinionated platforms;
- While the platform supports AI capabilities, it requires slightly more manual configuration to achieve advanced agentic behaviors compared to AI-native tools;
- The sustainable use license is very permissive, but not entirely open-source. White-labelling n8n or providing public cloud solutions is not allowed under this license.
Pricing
- Cloud version starts at 24€/month
- Custom pricing for enterprise customers (with discounts for eligible startups)
- Community edition is free for self-hosted deployment
Dify
AI agent builder type: Workflow-based agent builder
Best for: rapid prototyping and deployment of AI applications with minimal technical overhead
Dify is an open-source platform for building generative AI applications. It combines Backend-as-a-Service with LLMOps capabilities to make AI development accessible to both technical and non-technical users. Dify's comprehensive approach includes visual workflow orchestration, RAG pipelines and flexible publishing options, enabling users to quickly move from concept to production.
Unique capabilities
- Easy to use pre-configured agentic features, like document processing, vector search, and knowledge base integration;
- Built-in publishing capabilities: deploy single-page Web Apps, website widgets or via API.
Limitations
- Dify’s pre-configured approach may not suit highly specialized AI behaviors or complex integration patterns.
- As a relatively new platform, it may lack the maturity and extensive ecosystem of more established alternatives.
Pricing
- Paid plans starting at $59 per month for the Professional
- Enterprise pricing is available upon request
- Free cloud-hosted Sandbox plan and self-hosted Community version
Vellum
AI agent builder type: Workflow-based agent builder
Best for: teams requiring production-grade AI development
Vellum is an enterprise-focused AI development platform for building, testing and deploying AI applications at scale. The platform provides several purpose-built tools, including sophisticated prompt engineering capabilities, evaluation frameworks and deployment management. Vellum's architecture supports both GUI-based development and SDK integration.
Unique capabilities
- 1:1 code – interface synchronization between visual workflow design and underlying code implementation;
- Built-in evaluation framework with test-case bank;
- Deployment management system with version control and monitoring.
Limitations
- While the Vellum SDK part is open-source, the whole platform is not, which increases the risks of vendor lock-in.
- Vellum supports multiple LLM providers, including OpenRouter, Vertex AI, AWS Bedrock, however, no indication for self-hosted LLM support.
Pricing
- Prices for both Growth and Enterprise plans are not publicly available
- 7-day free trial
Camunda
AI agent builder type: Workflow-based agent builder
Best for: enterprises organizations looking to integrate AI agents into existing business process management workflows
Camunda takes a different approach to AI agent development by retrofitting AI capabilities into its traditional Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) framework. Specifically, by creating ad-hoc subprocesses with non-deterministic AI behavior inside otherwise deterministic business processes. This way organizations are able to maintain their existing process management practices while incorporating modern AI capabilities.
Unique capabilities
- Workflow creation via BPMN notation sets Camunda apart from other AI agent builders.
- Composable orchestration design and a decade-long process automation experience provide mature integration capabilities and enterprise-grade reliability.
Limitations
- Camunda's BPMN-centric approach may present a learning curve for teams unfamiliar with business process modeling concepts.
- The platform's enterprise focus means it may be overly complex for simple AI agent use cases that don't require extensive process orchestration.
Pricing
- Free version for development and testing
- Custom enterprise pricing
LangGraph
AI agent builder type: Non-workflow-based agent builder
Best for: developers requiring maximum control over complex, stateful AI agent architectures
LangGraph is a low-level orchestration framework designed for building, managing and deploying long-running, stateful AI agents. Built by the LangChain team, LangGraph extends beyond traditional chain-based approaches to enable sophisticated agent workflows involving cycles, controllability, and persistence.
Unique capabilities
- Tight integration with the broader LangChain ecosystem;
- Vast array of pre-built components, tools and model integrations.
Limitations
- Requires significant technical expertise and programming knowledge;
- Complex pricing structure, as LangGraph requires other LangChain products for production use (e.g. LangSmith subscription for observability).
Pricing
- Developer plan with free access (limited to 1M nodes executed per year)
- Plus plan with 39$ per seat / month and additional usage-based pricing
- Custom Enterprise plan
Restack
AI agent builder type: Non-workflow-based agent builder
Best for: Developers building production-ready AI agents that require long-running processes and advanced reliability features
Restack is a backend framework for building reliable AI agents that can operate in production environments. The platform addresses common challenges in AI agent deployment such as failure recovery, long-running processes and state management. Restack supports development in both Python and TypeScript, providing flexibility for diverse development teams.
Unique capabilities
- Restack adopted Daniel Kahneman's dual process theory, implementing a split approach to agent behavior that balances fast, intuitive responses with slower, deliberate reasoning
- The platform's architecture supports long-running workflows that can operate for days, months or years with built-in failure recovery and state persistence.
Limitations
- Restack requires programming expertise in Python or TypeScript, making it inaccessible to non-technical users.
- The platform's focus on backend infrastructure means it requires additional frontend development for complete user-facing applications.
- As a new platform, it may lack the extensive community and ecosystem of more established alternatives.
Pricing
- Cloud tiers with per-seat pricing and additional expenses for cloud computing
- Custom Enterprise pricing
- Open-source library for self-hosted deployment
Autogen
AI agent builder type: Non-workflow-based agent builder
Best for: Research and development teams requiring sophisticated multi-agent coordination and conversation management
Autogen is a framework from Microsoft for building AI agents and applications. The platform’s modular architecture includes a Core component, several specialized modules for different use cases and an AgentChat for creating conversational AI systems.
Unique capabilities
- The recently upgraded Autogen Studio provides a low-code prototyping environment on top of AgentChat that makes multi-agent development more accessible to a broader audience.
- The platform's modular design allows developers to compose complex agent interactions while maintaining clear separation of concerns across different agent capabilities.
Limitations
- Autogen requires programming expertise in Python 3, which makes multiple use-cases outside conversational AI inaccessible to non-technical users.
- The platform's academic origins may result in a steeper learning curve for business-focused implementations and fewer learning resources due to a smaller developer community.
Pricing
- Open-source free library
How to choose an AI agent builder?
Selecting the optimal AI agent builder requires balancing several factors for long-term success.
Here's what technical teams should prioritize:
Ease of use
Match the complexity of the platform to the skill level of your team. For business teams, no-code builders like Dify and Vellum offer drag-and-drop interfaces requiring minimal coding. More tech-savvy teams benefit from n8n's hybrid approach, which combines visual workflows with JavaScript/Python code extensions.
AI capabilities
Prioritize model flexibility and built-in evaluation frameworks. Most platforms already support multiple LLM vendors, allowing you to mix providers like OpenAI, Anthropic and OpenRouter. Vellum stands out with its built-in evaluation framework and test-case banks, while n8n recently introduced workflow evaluation nodes. Verify local deployment options for sensitive data with platforms like n8n, Autogen and Restack, as this becomes crucial for compliance and data sovereignty requirements.
Integrations
Mature enterprise-grade tools like n8n and Camunda provide hundreds of pre-built connectors to CRMs, databases and legacy systems. Modern frameworks are increasingly adopting Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP) to integrate with various services, providing a standardized approach to agents’ tool connections. Avoid platforms requiring custom middleware for common tools like Slack or ServiceNow.
Future proof
Choose established platforms that balance innovation with stability. While many AI agent builders like Dify and Vellum are relatively new companies, prioritize those that adopt emerging industry standards and demonstrate commitment to long-term development. Open-source or self-hosted solutions (like n8n's Community edition, Autogen or Restack) help prevent vendor lock-in – particularly important given the volatility in the AI startup space. For production deployments, focus on platforms with proven track records, active communities and transparent roadmaps rather than chasing the latest features.
Cost & value
Analyze total ownership costs beyond the surface price. Most platforms combine seat-based pricing (Vellum, Restack, LangGraph), usage-based charges for workflow executions (n8n) or compute consumption (Restack). AI model costs are either included in monthly limits (Vellum, Dify) or bring-your-own-key pay-as-you-go (n8n, Autogen). Cloud platforms include potential hidden costs like premium features or scaling limitations. Open-source options like n8n's community edition and Autogen eliminate vendor fees but require infrastructure management.
Evaluate pricing models against your expected usage patterns - high-volume deployments often benefit from self-hosted solutions, while low-volume experimentation suits cloud plans with included AI credits.
Wrap up
In this guide, we’ve evaluated 7 AI agent builders in two main categories:
- Workflow-based builders: n8n, Dify, Vellum and Camunda for visual development with enterprise integrations
- Non-workflow frameworks: LangGraph, Restack and Autogen for maximum flexibility and developer control
For enterprises looking to deploy AI agents in production environments, the choice often comes down to balancing ease of use, control and integration capabilities. Workflow-based builders excel at automating existing business processes with appropriate guardrails, while non-workflow frameworks provide the flexibility needed for novel use cases requiring custom agent architectures.
n8n stands out by offering both approaches in a single platform. It allows teams to start with visual workflows and progressively add custom code where needed, all with 400+ pre-built integrations and more than a thousand community nodes. While not the simplest tool for building AI agents from scratch, n8n excels in complex, highly integrated use cases. Its intuitive interface and rich templates provide fast value, but its real strength lies in enabling sophisticated, deeply connected systems.
What's next?
Ready to build your first AI agent? Here’s how to get started:
Explore AI agent implementations:
- Learn the fundamentals of AI agents and their practical applications
- Discover 15 real-world AI agent examples across different industries
- Follow a step-by-step guide to building your first AI agent
Get hands-on with n8n:
- Explore n8n’s AI capabilities and integration ecosystem
- Browse AI workflow templates for inspiration
- Deploy locally with the Self-hosted AI Starter Kit for privacy-first solutions
Deepen your AI knowledge:
- Compare LlamaIndex vs LangChain for RAG applications
- Develop an AI adoption strategy for enterprise environments