Make and Zapier are two of the most popular automation platforms. With their help, you can connect various apps and services and create powerful workflows.
In this article, we'll provide an in-depth comparison of Make vs Zapier, focusing on key aspects such as pricing, integrations, user management, API capabilities, error handling, scalability, AI automation, and others.
And there is more – we'll take a close look at n8n, a source-available workflow automation tool. We’ll see what makes it a powerful alternative to both Make and Zapier, and compare its features with those of the two platforms.
TL;DR
Although Make and Zapier offer similar functionality, there are distinct differences that may make one better suited to your needs than the other. Zapier is a good starting point for non-tech users who are exploring automation, while Make is more robust for building advanced scenarios.

- Pricing: both Make and Zapier charge per individual operation, whereas n8n charges only per workflow execution.
- Pre-built connectors: Make has 1500+, Zapier has 6000+, n8n offers 1000+ (some of them require additional credentials set up). All three platforms allow you to make custom requests, but n8n has easier ways to do this.
- Compared to Zapier, Make has more robust error handling, collaboration, and user management features, especially on higher-tier plans. n8n supports basic team management on paid tiers and extended functionality on the Enterprise plan.
- Make is better suited for complex workflows and high data volumes; Zapier is easier to expand but has limitations in customization and handling complex workflows. n8n has unique nodes for data transformations and allows the creation of highly flexible workflows with multiple triggers.
- Coding: both Make and Zapier impose significantly limited custom scripting, while n8n could be much more attractive to developers.
Make vs Zapier – Which is the best?
| Feature | Make | Zapier |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing model | Charge for each individual operation |
Charge for each individual task |
| Number of pre-built connectors |
1500+ | 6000+ |
| Custom connectors | Yes, create custom apps and make custom HTTP requests |
Yes, via the Zapier Developer Platform or custom outgoing webhooks |
| Coding features | Built-in functions or limited custom JS functions on Enterprise plan |
Code by Zapier supporting JS and Python, with limitations |
| Error handling | Robust error handling options like ignore, resume, rollback, etc. |
Basic error handling steps |
| Collaboration | Sharing and exporting scenarios |
Sharing only on Team plan and above |
| User management | Advanced roles and permissions on Teams and Org levels |
Multiple users only on Team plan and above |
| Data storage | Data Stores feature similar to databases |
Tables feature to store and manage data |
| Customization and flexibility |
Designed to handle complex workflows |
Easy to expand, but limited customization and complex workflows |
| Ease-of-use and onboarding |
User-friendly interface, suitable for non-technical users |
Easiest to get started, ideal for beginners and non-technical users |
Make vs Zapier: A closer look
After comparing Make and Zapier at a high level, let's explore some of the key aspects that differentiate these two platforms.
Pricing
Key takeaway: Make is generally more affordable for complex workflows, while Zapier's pricing can increase quickly as your automations grow.
Make.com charges by operation. Each time a module in a scenario performs an action, it counts as one operation. The first module always counts as one operation, even if it doesn’t return a bundle (a data element). Router modules and error handlers do not count as operations.
Zapier charges by task in a similar fashion. A task is a single data element that has been successfully processed in a single action step.
For example, a Zap receives an email with a single attachment, uploads an attachment to Dropbox and sends a Slack message. In this case, the data flows through one Trigger, two action steps and consumes 2 tasks. If 10 emails arrive at once, the Zap will consume 20 tasks (10 tasks for each action step).
Certain things do not count as tasks, such as all Triggers (first step of each Zap), Filters, Paths and various internal actions like Formatter, Delay, Looping and some others.
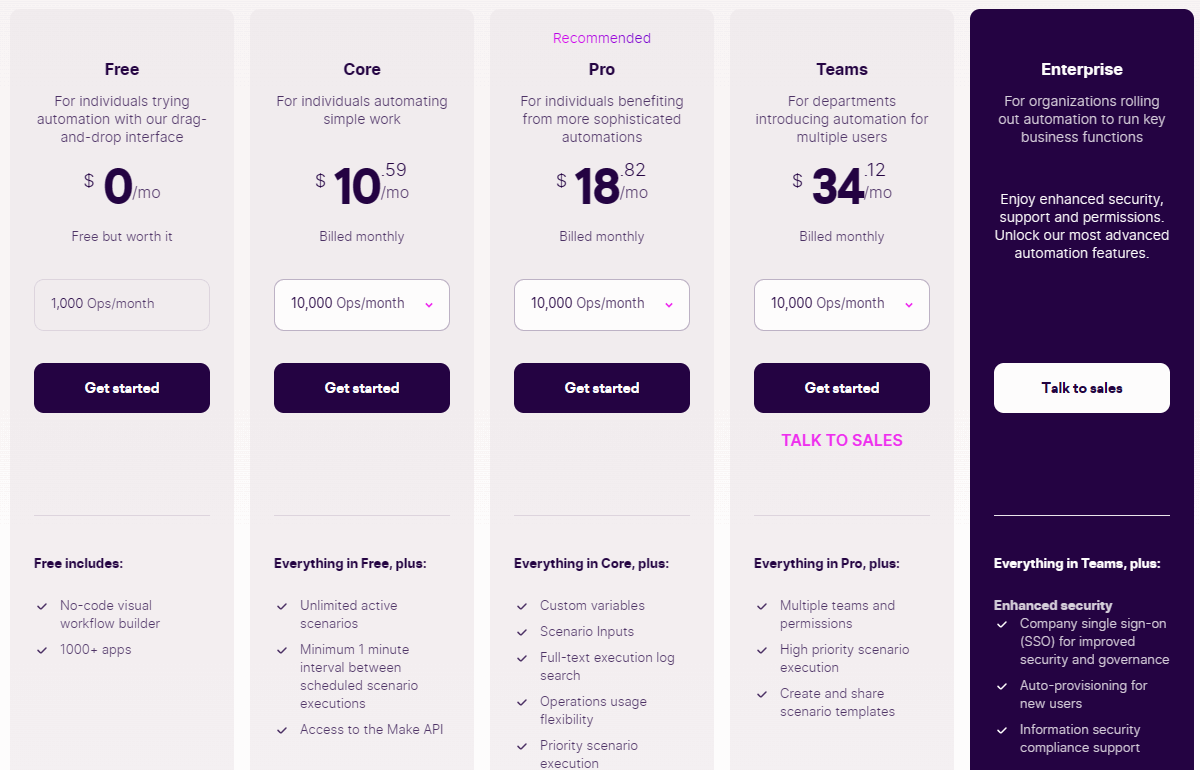
Finally, both Make.com and Zapier offer a modest free tier, but with significant feature gating even for basic functions. Make’s pricing is more affordable, whereas Zapier's costs skyrocket very quickly. Both platforms allow you to purchase ad-hoc steps and operations if you exceed their monthly quotas.
Integrations
Key takeaway: Make and Zapier offer a wide range of integrations, with Zapier having a larger library of pre-built apps. Both Make and Zapier allow for custom requests.
Make offers a library of over 1500 pre-built connectors for popular apps and services, as well as the ability to create custom connectors via various HTTP Modules. This allows users to integrate a variety of tools and platforms, even if they are not included in the Make library. There are seven HTTP Modules for different use-cases, so things can get pretty confusing rather fast.
Zapier, on the other hand, has an impressive library of more than 6000 pre-built apps, covering most of the common tools and services used by businesses. However, if a specific app is not available, users can send a custom request. This is done via a premium Webhook Action, meaning that it's completely not available for the free-tier users.
Both platforms have advanced developer portals for creating custom integrations via their Web UI.
User management
Key takeaway: Make and Zapier offer multi-user accounts, but Make supports a more advanced account management system with programmatic access via API.
Make supports organization accounts with unlimited users right from the start. The advanced Team features are available from the Team plan onwards. With a two-level role system (organization and team roles), there is enough granularity and control over the entire account. This allows organizations to assign specific permissions to each user based on their responsibilities and the level of access required. Finally, Make’s API supports programmatic control over the entire organization, including user management.
Zapier allows multiple users in a single account only on the Team and Enterprise plans:
- There are several basic roles for the Team account;
- Account users can share Zaps, folders and credentials;
- The Enterprise plan offers even more granularity, but at the time of writing, we could not test these features.
Coding features
Key takeaway: Zapier offers fairly limited coding capabilities in JS and Python. Make only supports custom JS scripting on the Enterprise plan, so all other users will have to rely on workarounds.
Make provides the following:
- Built-in functions for simple manipulations with strings, arrays and dates.
- Several logical operators are also supported.
- These functions work as snippets and have a non-standard syntax.
- However, looking at the functions' purpose, we can see that most of them have JavaScript equivalents and should be familiar to advanced users.
2. Custom JS functions are only available for Enterprise plan users and are subject to strict limitations: only ES6 version of JavaScript, no custom libraries, 300 ms execution time cap, max 5000 characters, no HTTP requests.
Zapier, on the other hand, supports custom scripting via the Code by Zapier action:
- Two languages are available: JavaScript (Node.js 14 modules + fetch) and vanilla Python (ver. 3.7.2).
- When working with the JS, users can perform data filtering, variable creation, advanced table lookups and data requests.
- StoreClient is a unique feature that supports the storage of small amounts of data between Zap runs.
- Zapier’s coding functionality has rather strict limits on input data. Scripts are run on AWS Lambda with an 6Mb I/O cap.
AI features
Key takeaway: Make and Zapier offer a variety of integrations with popular AI-services. AI-powered tools to improve workflow automation are also available on both platforms.
Make offers a wide range of AI integrations, including OpenAI (ChatGPT, Whisper, DALL-E), Google Cloud Vision, Eleven Labs, Eden AI and Cloudinary. These integrations allow users to perform tasks such as summarizing emails, personalizing messages, converting text to audio and much more.
Additionally, Make's AI Assistant helps users build scenarios by understanding natural language prompts and suggesting relevant modules.
Zapier has recently expanded the use of AI on its platform. Beyond connecting third-party AI services, Zapier offers several native features:
- Zap Guesser suggests automations based on user input;
- Copilot, an AI assistant that helps users build Zaps faster;
- The platform also offers AI-powered chatbots (in beta) to serve customers and employees, as well as AI fields in Zapier Tables for sentiment analysis and content summarization;
- Finally, Zapier Central (in preview) allows users to work with AI-powered bots that understand their business, while Canvas (in beta) enables users to visually map out processes and receive AI-recommended improvements.
Data storage and management
Key takeaway: Both Make and Zapier offer built-in data storage options, but they differ in their approach and flexibility.
Make offers a feature called "Data stores" that allows users to store and manage data within the platform. The data stores in Make are similar to simple databases and allow users to add, replace, update, retrieve, delete, search and count records. Users can create multiple data stores, each with its own data structure, and allocate storage space from their total internal data storage capacity, which varies based on their plan.
Zapier also offers data storage via Zapier Tables, which allows users to store and manage data directly on the platform. Zapier Tables provides a user-friendly interface for creating tables, adding records and integrating with other apps and workflows.
While both platforms offer built-in data storage, Make's data stores offer more flexibility and control over data structure and storage allocation. However, users need to be aware of the challenges that come with updating the data structure in Make and should always create backups before making significant changes.
Error handling and monitoring
Key takeaway: Both platforms offer error handling and monitoring capabilities, but Make offers advanced options for customizing error handling scenarios, saving incomplete executions, and managing email notifications.
Make offers robust error handling features, such as setting up error handlers to deal with errors or unexpected events in your scenario. Users can choose from five error handlers:
- Ignore
- Resume
- Commit
- Rollback
- Break.
Make also allows incomplete executions to be saved when an error occurs so that users can investigate and resolve issues. Additionally, Make provides customizable email notifications for warnings, errors and scenario deactivations due to errors.
Zapier provides options for error handling, including the ability to add error handling steps to each step in a Zap (except for the Trigger and Paths steps). These error handling steps allow users to customize how their Zaps run when an error occurs. Zapier also offers manual and automatic replay options for failed Zap runs. However, Zapier's error handling capabilities may not be as extensive as Make's, especially when it comes to customizing error handling scenarios and storing incomplete executions.
Collaboration and sharing
Key takeaway: Make enables sharing and exporting workflows, facilitating collaboration and reusability, while Zapier's sharing options are limited to the Team plan.
Make allows users to share and export their workflows, making it easier for team members to collaborate and reuse successful automation templates. This can be particularly useful for organizations with multiple departments or teams working on similar processes.
Sharing Zaps through Zapier is only available from the Team plan onwards, which may limit collaboration opportunities for users on lower-tier plans. Similarly, Zap export / import only works on the Teams and Enterprise plans.
Customization and flexibility
Key takeaway: Both platforms offer customization options. While Make offers a more flexible and extensible environment for complex workflows, Zapier stands out with several complementary features that extend basic automations.
Make is designed to handle complex workflows and allows moving larger volumes of data at the same budget, offering a scalable and extensible platform. Users can create custom modules, use built-in functions, and leverage the API for further customization. The enterprise plan includes an on-prem module for clients and a mobile app for automating actions on the end-user device.
Zapier also offers customization options, such as Code by Zapier and the ability to create custom integrations. However, Zapier can face challenges when dealing with highly complex workflows or large amounts of data, as there are some limitations on execution time and memory usage for custom code. On the other hand, Zapier offers services such as Interfaces, Chatbots and Canvas. With these tools, users can extend the basic functionality and create apps or collaborate on automating business processes.
Make and Zapier alternative: n8n
While Make and Zapier are both powerful automation platforms, there is another alternative worth considering: n8n – a source-available workflow automation tool.
Overview: Make vs Zapier vs n8n

Zapier and Make have given millions of ordinary users superpowers, enabling them to automate tasks – something that was previously only possible for developers. With the huge community, abundance of training material and ease of access, these platforms are true leaders in their fields.
n8n was originally developed as a tool to help developers avoid repetitive and tedious tasks such as setting up environments and servers, configuring credentials and sifting through API docs. Soon after its launch, many people appreciated the node-based interface and the ability to easily connect services without any coding (although coding was always a strong point of n8n).
In 2024, n8n already achieved feature parity with Make and Zapier when it comes to automation, offering several unique characteristics not found in these two platforms. The main difference of n8n lies in these areas:
- Licensing and pricing;
- Enterprise readiness;
- Coding and developer tools;
- Scalability and extensibility;
- AI-capabilities for making complete services (chatbots, agents, RAG, vector store, custom tools and more).
Licensing and pricing
n8n comes with a fair-code source-available license. This means that anyone with the appropriate knowledge can self-host it or even inspect the product codebase.
In terms of pricing, n8n offers several cost-effective options. Although there’s no free tier for the cloud offering (apart from a trial period), only workflow executions are charged.
For some automations, n8n can be 1000 times more cost-efficient compared to Zapier or Make. Only a fraction of users who have very modest requirements would find n8n more expensive compared to alternative platforms.
On top of that, there is no feature gate on core functionality: no premium nodes, all users are equally able to build complex workflows regardless of their pricing plan. At the higher tiers, users have more options for team collaboration or advanced enterprise features, but the workflow-building experience is the same for all users.

Enterprise readiness
Although n8n offers a completely free option for self-hosting, its true value lies in an Enterprise offering.
Organizations have everything they need to roll-out an on-prem version of n8n, including: advanced security features and audit logs.
- External secrets vault: n8n's integration with external secrets stores (like HashiCorp Vault) centralizes sensitive data management, enhances security, and streamlines compliance.
- RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) in n8n enhances efficiency and security by enabling granular access management within team environments.
- Environments & version control - n8n utilizes GitHub for rigorous version control across production and non-production environments, minimizing deployment risks and promoting stable, continuous innovation.
- n8n's Queue Mode enhances scalability by distributing workflow executions across multiple worker instances, dynamically adjusting capacity to meet demand and optimize resource use.
This is an especially sought-after set of features that are not available in Zapier or Make. This makes n8n an ideal product for supporting even the most business-critical operations in regulated industries.
Startups are also eligible for a dedicated plan.
Coding and building products
The no-code side of n8n is complemented by a strong ability to write code and even build complete products. Let’s see what developers might find particularly appealing about n8n.
First, n8n supports expressions. These seemingly short JS snippets can save a lot of time and help design effective workflows thanks to the built-in support of Luxon and JMESPath libraries. Both data transformations and node settings support expressions. This makes workflows robust and compact, avoiding unnecessary IF switches.
Second, is the Code node. Here you can write custom logic and advanced functionality in JavaScript or Python. Users that run n8n in self-hosted mode can even install 3rd-party npm libraries, access filesystem and make HTTP requests.
Take a look at the screenshot of a real project. In this example, the Code node has access to an external npm library (nunjucks) and writes a file directly to the filesystem.
Scalability and extensibility
We’ve already covered the possibility of extending n8n with npm packages. But that’s just scratching the surface:
- You can give n8n access to custom system tools or fully integrate it into your systems.
- n8n can run as a single instance or in a robust queue mode.
- Ultimately, you can roll out n8n on a Kubernetes cluster.
When it comes to extending nodes, n8n enables the creation of community integrations for third-party services or nodes that improve workflow building experience.
Creating AI-powered products
Last but not least, if you want to create an AI-powered project, n8n offers you a good solution with LangChain support. Almost 70 dedicated nodes allow you to build a complete back-end for:
- LLM-chatbots;
- OpenAI assistants;
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) workflows with in-memory storage or vector databases (Supabase, Qdrant, Pinecone and Zep);
- AI-powered agents (conversational, function calling, plan and execute, ReAct);
- Custom tools (including n8n-workflows as tools);
- Simple workflows with document loading, text splitting and embeddings.
While building these products, you can use popular LLMs from OpenAI, Antropic, Mistral and HuggingFace, or custom model endpoints including completely self-hosted LLMs.
As usual, there’s a special node for custom code that supports the langchain.js library.
Comparison table of Make, Zapier, and n8n
To help you compare n8n with Make and Zapier, here's a table highlighting some of the key features and differences:
| Feature | n8n | Make | Zapier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing model | Charge per workflow, no limit on tasks / steps |
Charge for each individual operation |
Charge for each task |
| Self-hosting | Yes, free tier and Enterprise |
No | No |
| Custom connectors |
Yes, via HTTP node (easy) OR write and deploy your own n8n nodes (advanced) |
Yes, create custom apps via Web UI and make custom HTTP requests |
Yes, via the Dev Platform or custom outgoing webhooks with some limits |
| Coding features | Built-in JS/Python support, install external packages when self-hosting |
Limited custom JS functions only on Enterprise plan |
Code by Zapier supporting JS and Python, with limitations |
| Error handling | Customizable error handling workflows |
Robust error handling options like ignore, resume, rollback, etc. |
Limited error handling steps |
| Collaboration | Sharing and exporting workflows and credentials from Starter tier |
Sharing and exporting scenarios |
Sharing only on Team plan and above |
| User management |
Unlimited number of users on all plans, basic user management from Pro tier |
Advanced roles and permissions on Teams and Org levels |
Multiple users only on Team plan and above |
| AI features | AI-driven workflows via LangChain and Ask AI to generate code |
Common AI integrations and an AI-powered tool for making scenarios |
AI-powered Zap builder, Formatter with AI, Code with AI |
| Data storage | Only small amount of data is stored as part of the workflow |
Data Stores feature, similar to databases |
Zapier Tables feature to store and manage data |
| API | Available on all plans, mostly workflow and execution functionality. Limited user management via API |
API with advanced features including credentials and user management |
Observability API only on Enterprise plan |
| Enterprise offering |
Dedicated enterprise plan with enhanced security and unlimited workflows |
Enterprise plan with custom pricing |
Enterprise plan with an annual task limit |
| Scalability and extensibility |
Highly scalable and extensible, requires additional configuration |
Designed to handle complex workflows and high volumes of data |
Easy to expand, but limited customization and complex workflows |
| Community and support |
Active community forum that includes feature requests voting and bug-reports. This ensures swift updates and fixes. |
Community support, company support on paid tiers. Extensive documentation, including the Academy |
Community support, premier support for higher plans, learning platform |
| Workflow management |
Branching, looping, merging data, dataset comparison and error handling within workflows |
Complex workflows with tools like Router module and error handling |
Multi-step Zaps and paths for conditional logic, but limited compared to n8n and Make |
| Data transformation |
Powerful JS expressions, nodes for seamless data conversion and a custom code for advanced cases |
Wide range of built-in functions for data transformation |
Formatter and Code steps for data manipulation, with limitations |
Wrap Up
In this article, we’ve thoroughly compared Make and Zapier – powerful automation platforms with their own strengths and weaknesses.
n8n emerges as a compelling alternative, especially for users who value cost-effectiveness, robust workflow building experience and developer-friendly features.
The choice of the platform depends on various factors, including the complexity of your automations, the integrations you require, the initial skills of your team and your budget.



FAQ
Is Zapier the same as Make?
While Zapier and Make (formerly Integromat) are both automation platforms that connect different apps and services, they have some important differences.
Zapier focuses on simplicity and ease of use, offering a wide range of pre-built integrations and templates. In addition, Zapier has introduced several new features to its platform, such as Tables, Interfaces and Chatbots.
Make, on the other hand, offers more advanced features and flexibility, allowing users to create complex workflows and custom scenarios.
What are the limitations of Zapier?
One of Zapier's main limitations is its pricing structure. As your automations grow, the cost of using Zapier will increase significantly.
Zapier also has some limitations on the number of tasks and volume of data you can process, depending on your plan. Some users may also find Zapier's interface and workflow editor less flexible compared to other automation platforms like Make or n8n.
Can I trust Zapier?
Zapier is a well-established and respected automation platform that has been on the market since 2011. It has demonstrated its commitment to data privacy and compliance with applicable laws and participates in the EU-US Data Privacy Framework program.
It's important to understand that when using Zapier, you are considered the "data controller" and are responsible for complying with data protection laws. Zapier is responsible as a "data processor" for protecting the data that flows through its systems.
Is Zapier free of charge?
Zapier offers a modest free plan that allows you to create simple 2-step Zaps with limited features and task runs. This plan is only sufficient for occasional use or testing.
In most other cases, your automations will require an upgrade to a paid plan. Lower-tier paid plans are quite affordable. However, as your operations grow, you may see a steep price increase, which can be very burdensome, especially for small businesses or individuals.
Is Zapier worth the cost?
Whether Zapier is worth the cost depends on your specific needs and budget. In our experience, it’s easy to estimate the automation of transactions with a known ROI. One example is the processing of sales orders.
If you are automating routine tasks and especially trying to perform bulk data transfers, alternatives such as n8n may significantly outperform Zapier.
What’s next?
Now that you better understand the differences between Make and Zapier you can pick the right tool!
Or perhaps give n8n a try?
-> Make vs n8n
-> Zapier vs n8n
How to move to n8n from Make?
Migrating from Make to n8n is relatively straightforward, however there are currently no ready-made 1-click tools to translate Make scenarios into n8n workflows.
To start transferring scenarios, sign up for an n8n account, familiarize yourself with the workflow editor and view the documentation page. A quickstart guide and 2-level course will help you to get started.
n8n offers a wide range of nodes (integrations) covering most of the popular apps and services supported by Make. Custom integrations can be done via the HTTP node. If you have used functions in Make, then most of them have JavaScript expressions as equivalents.
Not all Make connectors are identical to the n8n nodes, so feel free to ask in a community forum for the best approaches.
How to move to n8n from Zapier?
Switching from Zapier to n8n is similar to switching from Make. Most likely, transferring Zaps will be easier due to its lower complexity.
However, you may encounter some hurdles if you make extensive use of other Zapier tools such as Tables, Interfaces or Chatbots.
Re-creating Zapier Chatbots is the easiest task among these three thanks to the powerful LangChain integration in n8n. There are currently no equivalents for Tables and Interfaces in n8n. This may seem like a downside at first glance, but it also means that you are not vendor-locked to a specific solution.
We can recommend trying out some of the no-code databases (such as NocoDB, Baserow, or SeaTable). They are all available in the cloud and via self-hosting and also offer certain features similar to Zapier interfaces. Airtable is another option, although it’s only available as a cloud SaaS.
Join the community forum and share your success or seek support! Remember, the key to successful automation is to start small, iterate often and always keep learning.